How to use a transistor as a switch Circuit Diagram
How to use a transistor as a switch Circuit Diagram Introduction Transistors are often used as electronic switches, to control loads which require high voltage and current from a lower voltage and current. The most common example you'll see of this in a physical computing class is to use an output pin of a microcontroller to turn on a motor or other high current device. Here's how to set up both the BJT and the MOSFET transistor as a switch so you can easily control things like motors, lamps, and more.

However, if you are delivering power to an entire circuit or a voltage-sensitive device, then you want to use a high-side switch. By the way, there are off-the-shelf components called " load switches." These ICs have a P-Channel MOSFET as the switching transistor with a built-in driver for that P-Channel. Electronics Tutorial about the Transistor as a Switch and using the Transistor as a Switch to operate relays, motors, lamps and other such loads
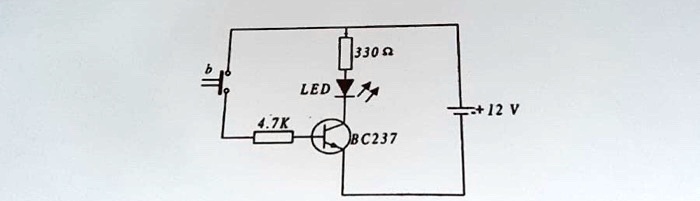
Using Transistor Switching Circuit Diagram
These pins are meant to send control signals, not to act as power supplies. The most common way to control another direct current device from a microcontroller is to use a transistor. Transistors allow you to control the flow of a high-current circuit from a low-current source. Video: Transistor Schematics Video: Meet the motors For the transistor to operate as a switch, a principle of the small base current controlling the large collector load current is used. If you want to control large currents, use the Darlington transistor as a switch Figure 7 shows the basic circuit for using a transistor to control a high-current load. You connect a DC power source to one terminal of the load, then connect the second terminal of the load to the collector of the transistor (or drain, for a MOSFET) of the transistor.

When we need to switch moderate to high levels of power, one of the best methods we can use is a transistor with an open-collector output. In this setup, we connect the emitter terminal of the transistor directly to ground.
